Table of Contents
Scenario planning & scenario thinking
(see updated notes at scenario_planning)
in “Why Scenarios?” http://www.gbn.com/about/scenario_planning.phpScenarios are not predictions. Rather, they are provocative and plausible accounts of how relevant external forces — such as the future political environment, scientific and technological developments, social dynamics, and economic conditions — might interact and evolve, providing our organizations with different challenges and opportunities.
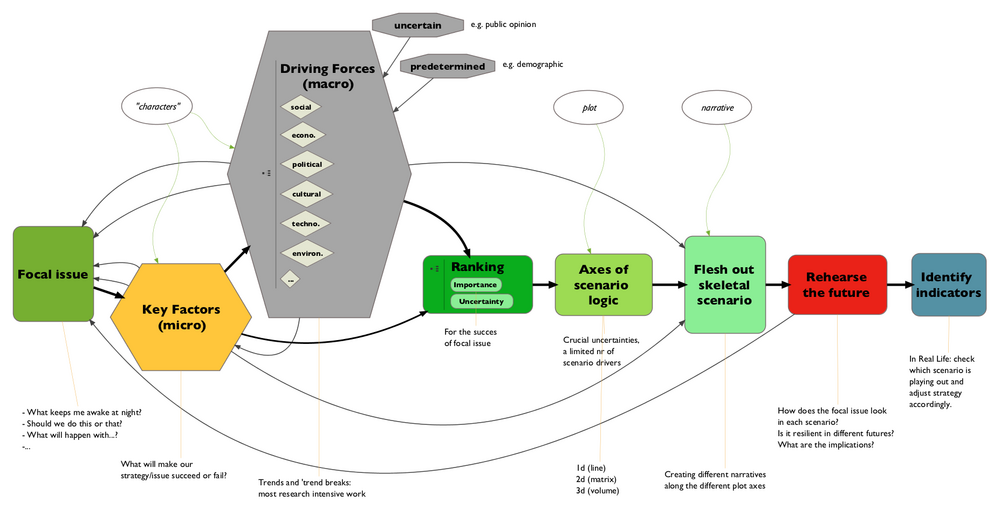
How to Build Scenarios
Scenario planning derives from the observation that, given the impossibility of knowing precisely how the future will play out, a good decision or strategy to adopt is one that plays out well across several possible futures. To find that “robust” strategy, scenarios are created in plural, such that each scenario diverges markedly from the others. These sets of scenarios are, essentially, specially constructed stories about the future, each one modeling a distinct, plausible world in which we might someday have to live and work. Yet, the purpose of scenario planning is not to pinpoint future events but to highlight large-scale forces that push the future in different directions. It's about making these forces visible, so that if they do happen, the planner will at least recognize them. It's about helping make better decisions today.
From How to Build Scenarios by Lawrence Wilkinson
Open source scenarios
Imagine a database of thousands of items all related to understanding how the future could turn out. This database would include narrow concerns and large-scale driving forces alike, would have links to relevant external materials, and would have space for the discussion of and elaboration on the entries. The items in the database would link to scenario documents showing how various forces and changes could combine to produce different possible outcomes. Best of all, the entire construction would be open access, free for the use. As a result, people around the world could start playing with these scenario elements, re-mixing them in new ways, looking for heretofore unseen connections and surprising combinatorial results. Sharp eyes could seek out and correct underlying problems of logic or fact. Organizations with limited resources and few connections to big thinkers would be able to craft scenario narratives of their own with a planet's worth of ideas at their fingertips.
in “Open Source Scenario Planning” http://openthefuture.com/2006/08/otf_core_open_source_scenario.html and http://www.worldchanging.com/archives//004246.html
Open foresight
“What is Open Foresight? We recently introduced the concept of ‘Open Foresight’ as a process we’re developing to analyze complex issues in an open and collaborative way, and to raise the bar on public discourse and forward-focused critical thinking […] In simple terms, open foresight is a process for building visions of the future together.”
Scenarios & dialogue
The ideal approach to the future combines free speculation and data-driven deduction. Scenarios are an ideal tool for strategic dialogue – Karl Schroeder
What next for scenario planning?
Recently I have been interviewing a variety of high profile futurists and up-and-coming strategists on how online approaches are transforming scenario planning and futures work.
Scenarios
- They're provocative – they push the readers to think about possibilities they'd often rather not face. While this often means confronting unpleasant outcomes, it can also mean admitting the possibility of success, what it would take to get there, and what one would do if it happened.
- They're plausible – they make use of real-world facts and models to construct a set of futures that could actually come about. This is important, especially for organizations trying to make the world face up to the challenges in front of it.
- They're broad – while they usually have a specific issue as a focal question, they can't simply look at the actions of the organization or group at the issue's heart. Good scenarios look at the context of an issue, and examine changes across a wide spectrum of concerns.
- They're diverse – they acknowledge that the future is ultimately unknowable, so the best way to plan for what will really happen is to think about broadly different possibilities. This was, for me, the singular failing of the Pentagon abrupt climate change scenario – it only told one story.
- Finally, they're open – even readers not directly involved with the issue at hand can start thinking about their own choices and plans as shaped by the scenario narratives.
Reference
- Scenario planning resources. a well organised collection of texts, studies and references. http://www.well.com/~mb/scenario_planning/
- Slideshow on building scenarios by futuresavvy.com: http://www.slideshare.net/adgo/scenario-building-workshop-how-to-build-and-use-scenarios
- “The Art of the Long View” by Peter Schwartz
Diagram prepared with VUE
related: future_preparedness